|
|
| (Eine dazwischenliegende Version desselben Benutzers wird nicht angezeigt) |
| Zeile 59: |
Zeile 59: |
| ===Geburtstagsparty=== | | ===Geburtstagsparty=== |
|
| |
|
| * Kombinaiton ohne Wiederholung für <math>n = 12</math>, <math>k= 6</math>: <math>\begin{align} | | * Kombination ohne Wiederholung für <math>n = 12</math>, <math>k= 6</math>:<br> <br> |
| K(12,6) = \binom{12}{6}&= \frac{12!}{(12-6)!6!}=\frac{12!}{6!6!}\\ | | |
| &= \frac{7\cdot\not 8^2\cdot\not 9 ^3\cdot\not{10}^2\cdot11\cdot\not{12}^1}{1\cdot\not2\cdot\not3\cdot4\cdot\not5\cdot\not6 }\\ | | <math>\begin{align} |
| &=7\cdot2\cdot3\cdot2\cdot11\cdot1 = 924\end{align}</math> | | K(12,6)=\left(\begin{array}{c} |
| * Permutation für <math>n=6</math>: <math>P(6) = 6!= 1\cdot2\cdot3\cdot4\cdot5\cdot6=720</math>
| | 12 \\ |
| * Permutation mit Wiederholung für <math>n=6</math> und <math>k_1=3</math>, <math>k_2=3</math> : <math>\begin{align}
| | 6 |
| P(6;3,3) = \frac{6!}{3!3!}=\frac{4\cdot5\not 6}{\not 6}=20
| | \end{array}\right) &=\frac{12 !}{(12-6) ! 6 !}=\frac{12 !}{6 ! 6 !} \\ |
| \end{align}</math>
| | &=\frac{7 \cdot \not 8^{2} \cdot \not 9^{3} \cdot \not 10^{2} \cdot 11 \cdot \not 12^{1}}{1 \cdot \not 2 \cdot \not 3 \cdot 4 \cdot \not 5 \cdot \not 6} \\ |
| | &=7 \cdot 2 \cdot 3 \cdot 2 \cdot 11 \cdot 1=924 |
| | \end{align}</math> |
|
| |
|
| ===Genua Wahl=== | | ===Genua Wahl=== |
| Zeile 134: |
Zeile 136: |
| <li><p>Kombinaiton ohne Wiederholung für <math>n = 7</math> Farben:</p> | | <li><p>Kombinaiton ohne Wiederholung für <math>n = 7</math> Farben:</p> |
| <p><math>K(n,2) = \binom{7}{2}= \frac{7!}{(7-2)!2!}=\frac{7!}{5! 2!}=\frac{6\cdot7}{2}= \frac{42}{2}= 21</math></p></li> | | <p><math>K(n,2) = \binom{7}{2}= \frac{7!}{(7-2)!2!}=\frac{7!}{5! 2!}=\frac{6\cdot7}{2}= \frac{42}{2}= 21</math></p></li> |
| <li><p>Kombination mit Wiederholung für <math>n = 5</math> Farben: <math>\begin{align} | | <li><p>Kombination mit Wiederholung für <math>n = 5</math> Farben: <br><br> <math>\begin{align} |
| K^{W}(n,2) = \binom{5+2-1}{2}&= \binom{6}{2}=\frac{6!}{(6-2)!2!}\\ | | K^{W}(n,2) = \binom{5+2-1}{2}&= \binom{6}{2}=\frac{6!}{(6-2)!2!}\\ |
| &=\frac{6!}{4!2!}=\frac{5\cdot6}{2}= 15 | | &=\frac{6!}{4!2!}=\frac{5\cdot6}{2}= 15 |
6 aus 49
 13 983 816
13 983 816
Angebotsmöglichkeiten
1. Unternehmen:  Kombination Preis/Menge nicht erlaubt:
Kombination Preis/Menge nicht erlaubt: 
2. Unternehmen:  Kombination Preis/Menge nicht erlaubt:
Kombination Preis/Menge nicht erlaubt: 
Insgesamt  Angebotsmöglichkeiten.
Angebotsmöglichkeiten.
Anzahl der Abweichungen

Arbeitsgänge

Blindenschrift

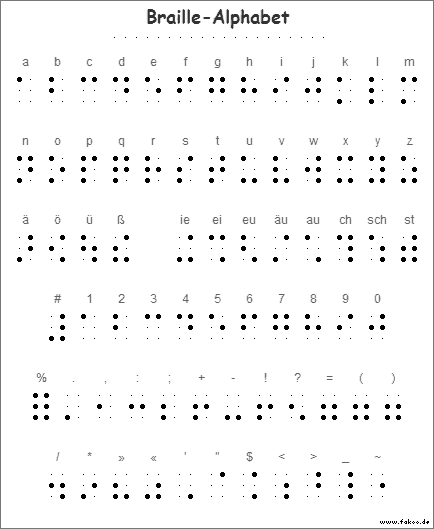
Quelle: http://www.siljakorn.de/braille-info.shtml
Bridge

Bücher

Bunte Häuser

Bunte Häuser

Camel Cup

- Unter den 22 100 Möglichkeiten sind 50 Möglichkeiten, die Testausritte mit genau einem Kamel zu machen;
 Möglichkeiten, die Testausritte mit 3 unterschiedliche Kamelen zu machen und folglich
Möglichkeiten, die Testausritte mit 3 unterschiedliche Kamelen zu machen und folglich  Möglichkeiten, die Testausritte mit zwei Kamelen zu machen.
Möglichkeiten, die Testausritte mit zwei Kamelen zu machen.
Code-Schlösser



Computerraum-Code
Anzahl aller Codes  (dritte Stelle
(dritte Stelle  )
)
Anzahl aller Codes  (zweite Stelle
(zweite Stelle  )
)
Anzahl aller Codes  (erste & vierte Stelle
(erste & vierte Stelle  )
)

Einmaleins

Geburtstagsparty
- Kombination ohne Wiederholung für
 ,
,  :
:

Genua Wahl
Nein, denn  Es hätte ungefähr der
Es hätte ungefähr der  millionenfache Betrag des Einsatzes gezahlt werden müssen.
millionenfache Betrag des Einsatzes gezahlt werden müssen.
Geschenke für die Abteilungsleiter

Hallenschwimmbad

Hemden

Lotto Toto

Orientierungsrundgang
- Permutation
 :
: 
- Permutation mit Wiederholung
 ,
,  :
: 
- 60 - 4
 3! = 36
3! = 36
Parkplätze

Pferdelotto

Pferderennen

Schachturnier

Schiffsignale

Schließfach
 Schließfächer
Schließfächer  falls “3” bzw. “5” bzw. “7” doppelt sind.
falls “3” bzw. “5” bzw. “7” doppelt sind.
Skatspieler
Nein, denn es gibt  64 512 240 mögliche Spiele. Der Skatspieler spielt
64 512 240 mögliche Spiele. Der Skatspieler spielt  Spiele/Jahr. Somit müsste er knapp
Spiele/Jahr. Somit müsste er knapp  Jahre spielen.
Jahre spielen.
TEA


Unfallstation




Wagenreihungen

Wanderwege
Variation mit Wiederholung für  Farben:
Farben: 
Kombinaiton ohne Wiederholung für  Farben:
Farben:

Kombination mit Wiederholung für  Farben:
Farben:

Zahlenschlösser

Zwei Würfel




